You might have been interested in tackling sonography jobs since you were in high school. Or, you’ve been exploring the wide world of healthcare careers, and becoming a sonographer caught your attention, and you are curious to know what does a sonographer do.
Regardless of how you made it to this stage, you’re fully committed to exploring the field. The first question is: what does a sonographer do?
Also, earning an average of $74,000 per year isn’t too bad either. If you’ve been looking for one career guide to rule them all, you’ve come to the right place.
Please keep reading for our full breakdown of everything you need to know about becoming a sonographer. We’ll also explore the different sonography careers you can choose from.
What Does a Sonographer Do?
Let’s start with the basics and work our way from there.
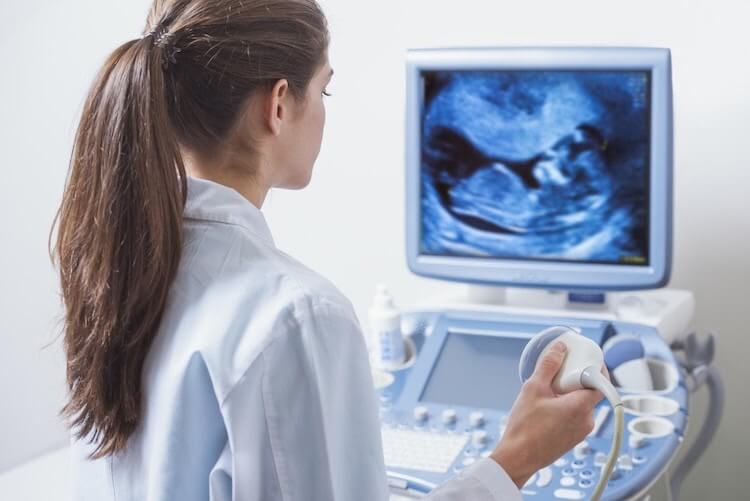
A diagnostic medical sonographer utilizes specialized equipment. It’s essential in creating pictures of the human body’s interior. These pictures are then presented on a watch for doctors to use in making diagnoses.
Sonographers use Ultrasound-emitting devices to check the status of a patient’s interior organs.
On the skin in the region being investigated, a sonographer administers a colorless and odorless gel. They place a tiny device called a transducer on the same skin area. This sends sound waves into the patient’s body.
These sound waves reverberate and form a picture. This picture is shown on a monitor and is used to diagnose illnesses. Also, it can assess the health of an organ or track the development of a pregnancy.
Ultrasounds, or sonographs, do not produce hazardous radiation. Unlike X-ray monitoring, which does. Thus, sonography is becoming a more popular area. As more individuals choose less invasive methods of monitoring within the human body.
What Are the Types of Sonography?
Diagnostic medical sonographers specialize in different areas of the body. After all, similar to surgeons and other medical professionals, specialization is key.
Here are some examples of different kinds of sonographers.
Diagnostic Cardiovascular (Cardio) Sonographer
Cardio sonographers are also known as echocardiographers. They assist cardiac doctors in diagnosing heart abnormalities. The device utilizes two-dimensional and three-dimensional pictures of the heart and its compartments.
Physicians examine the heart’s structure and blood flow. This helps with determining whether blockages or heart muscle degeneration. Doctors may use the images to recommend medication, surgery, or lifestyle changes.
The student may register to take the credentialing test. Those are given by either Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI). Or, the American Registry of Diagnostic Medical Sonographers. But, you’ll want to obtain the diagnostic cardiovascular sonographer certification (ARDMS) first.
Musculoskeletal Sonographer
The sonographer captures pictures of muscles. As well as ligaments, tendons, joints, and nerves throughout the body. They may use the pictures to check for joint problems as well as soft-tissue injuries.
Ultrasound technologists need to obtain the Registered in Musculoskeletal (RMSK) sonography certification. It provides value to the company, hospital, or private physician with whom they work.
Neurosonology Sonographer
A neurosonology sonographer is a highly specialized field of sonography. It uses a machine that differs from a standard ultrasound or sonogram.
Neurosonography is also known as neuroimaging. It uses specific beam shapes and frequencies from Transcranial Doppler (TCD) equipment. This is different from conventional obstetric and abdominal sonography devices. The TCD machine measures and monitors blood flow in the brain’s arteries.
Generally speaking, a clinician might search for neurological problems in newborns. Premature infants, those with a low birth rate, are common patients. That’s why certain neurosonographers specialize in neonatal brain imaging.
Abdominal Sonographer
An abdominal sonographer collaborates with physicians to scan the organs of the abdomen.
The sonographer must understand the abdominal region thoroughly. The sonographer is searching for anomalies. Things as tumors, stones, and tissue damage in the abdominal region.
The doctor examines the ultrasound pictures and provides therapy depending on the results.
Breast Sonographer
A breast sonographer is a professional that specializes in breast imaging. Breast imaging is typically done as a follow-up after an abnormal mammogram or clinical examination.
Sure, ultrasound cannot identify cancer. But, the technician and doctor may notice dark areas that are atypical in a healthy breast.
Obstetric Sonographer
An obstetric sonographer is a medical professional who specializes in imaging the fetus. Specifically, while it is still within the mother’s womb. They check for normal growth and development, as well as any anomalies or problems throughout pregnancy.
It is certain that, the sonographer’s job is to make sure the fetus and the mother are both healthy. The technician confirms the woman’s pregnancy. Then, they examine the developing fetus’s position and determines the due date.
Obstetric sonography is among the most frequent kinds of ultrasound.
Regular Duties of Sonographers
This is a career for those who are comfortable with directly dealing with patients. This brings us to the first responsibility of a sonographer, and that is their patient.
The patient is the sonographer’s primary priority. The preparation of the patient is the first step in her job. This involves explaining the ultrasound process to the patient. And confirming the patient’s identification. As well as collecting a thorough medical history by asking relevant questions.
The sonographer will next go through the process with the patient. Then, they’ll address any questions they may have.
Equipment Preparation
Next, we have the equipment preparation process. A sonographer’s pictures are only as excellent as the ultrasound equipment they use. Sonographers are in charge of keeping the equipment in top shape to perform at its best.
They may be in charge of arranging the usage of imaging equipment. In addition, you’ll be performing quality-control tests and making any required changes. They may also suggest further equipment acquisitions or upgrades.
Diagnostic Examination
Because ultrasounds emit no radiation, they are often used in obstetrics and gynecology. Sonographers may also be trained in cardiac, abdominal, vascular, neurological, or ophthalmic sonography.
In addition, the sonographer performs the ultrasound exam. They need to confirm that the pictures are clear. And, they cover the region being checked. Then, analyze the images and informs the physician of any abnormalities found.
Ready to Start Your New Healthcare Career?
When it comes to changing your career, things can be really overwhelming.
But, we hope that our guide has shed some light on what makes sonographers tick. As well as meeting your main question of “what does a sonographer do.”






